Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Impact of Antidiabetic Drugs on Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Han Na Jang, Sun Joon Moon, Jin Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Received October 16, 2023 Accepted January 3, 2024 Published online January 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1857 [Epub ahead of print]
- 884 View
- 39 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Inconsistent results have been reported regarding the association between the use of antidiabetic drugs and the clinical outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). This study aimed to investigate the effect of antidiabetic drugs on COVID-19 outcomes in patients with diabetes using data from the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) in South Korea.
Methods
We analyzed the NHIS data of patients aged ≥20 years who tested positive for COVID-19 and were taking antidiabetic drugs between December 2019 and June 2020. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to analyze the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 based on the use of antidiabetic drugs.
Results
A total of 556 patients taking antidiabetic drugs tested positive for COVID-19, including 271 male (48.7%), most of whom were in their sixties. Of all patients, 433 (77.9%) were hospitalized, 119 (21.4%) received oxygen treatment, 87 (15.6%) were admitted to the intensive care unit, 31 (5.6%) required mechanical ventilation, and 61 (11.0%) died. Metformin was significantly associated with the lower risks of mechanical ventilation (odds ratio [OR], 0.281; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.109 to 0.720; P=0.008), and death (OR, 0.395; 95% CI, 0.182 to 0.854; P=0.018). Dipeptidylpeptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) were significantly associated with the lower risks of oxygen treatment (OR, 0.565; 95% CI, 0.356 to 0.895; P=0.015) and death (OR, 0.454; 95% CI, 0.217 to 0.949; P=0.036). Sulfonylurea was significantly associated with the higher risk of mechanical ventilation (OR, 2.579; 95% CI, 1.004 to 6.626; P=0.049).
Conclusion
In patients with diabetes and COVID-19, metformin exhibited reduced risks of mechanical ventilation and death, DPP- 4i was linked with lower risks of oxygen treatment and death, while sulfonylurea was related to the increased risk of mechanical ventilation.

- Adrenal Gland
- A Novel Missense PRKAR1A Variant Causes Carney Complex
- Boram Kim, Han Na Jang, Kyung Shil Chae, Ho Seop Shin, Yong Hwy Kim, Su Jin Kim, Moon-Woo Seong, Jung Hee Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):810-815. Published online October 4, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1544

- 1,848 View
- 153 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The Carney complex (CNC) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by endocrine and nonendocrine tumors. Loss-of-function variants of protein kinase A regulatory subunit 1 alpha (PRKAR1A) are common causes of CNC. Here, we present the case of a patient with CNC with a novel PRKAR1A missense variant. A 21-year-old woman was diagnosed with CNC secondary to acromegaly and adrenal Cushing syndrome. Genetic analysis revealed a novel missense heterozygous variant of PRKAR1A (c.176A>T). Her relatives, suspected of having CNC, also carried the same variant. RNA analysis revealed that this variant led to nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. In vitro functional analysis of the variant confirmed its role in increasing protein kinase A activity and cyclic adenosine monophosphate levels. This study broadens our understanding of the genetic spectrum of CNC. We suggest that PRKAR1A genetic testing and counseling be recommended for patients with CNC and their families.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carney complex: A clinicopathologic study on a single family from several Canadian provinces
Alexandra Lao, Julio Silva, Brian Chiu, Consolato M. Sergi
Cardiovascular Pathology.2024; 69: 107599. CrossRef
- Carney complex: A clinicopathologic study on a single family from several Canadian provinces

- Calcium & Bone Metabolism
- Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Risk of Fractures and Falls According to Dosage and Interval: A Meta-Analysis
- Sung Hye Kong, Han Na Jang, Jung Hee Kim, Sang Wan Kim, Chan Soo Shin
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(2):344-358. Published online April 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1374
- 5,884 View
- 277 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
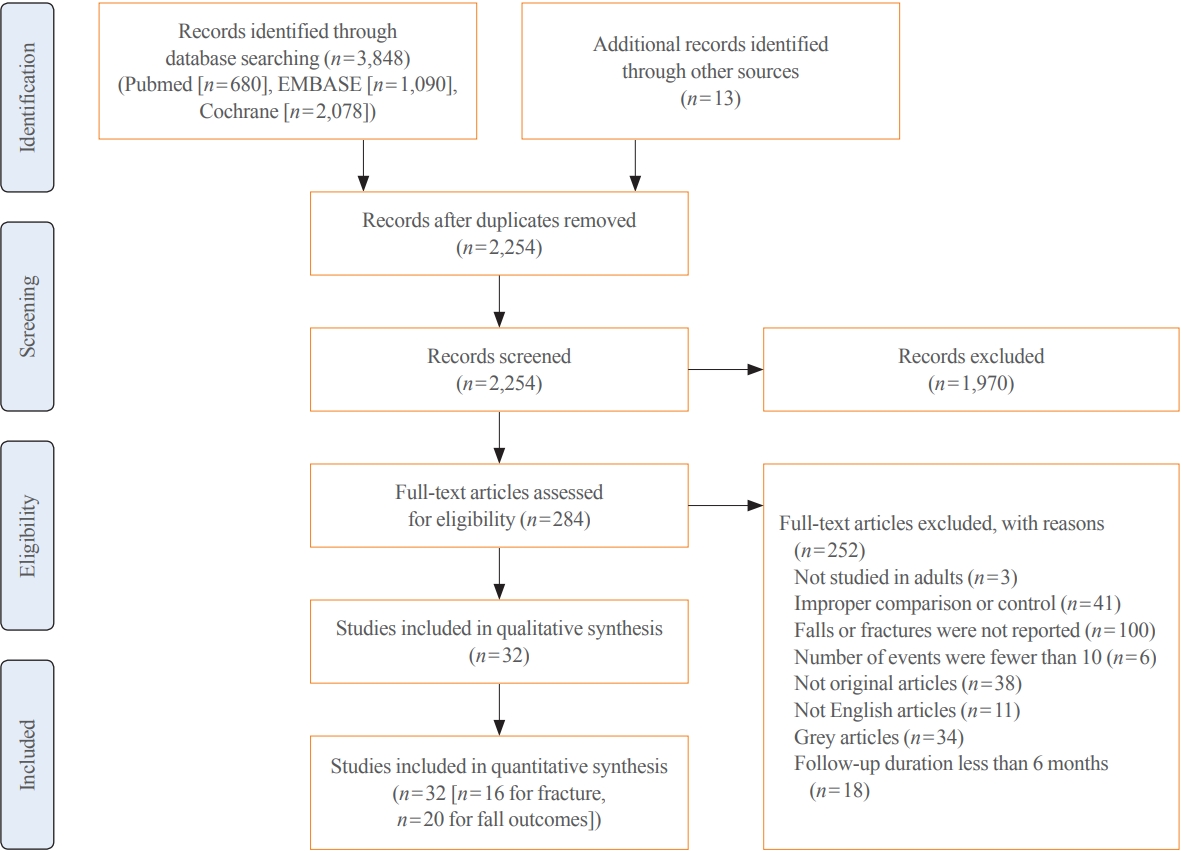
Although recent studies comparing various dosages and intervals of vitamin D supplementation have been published, it is yet to be elucidated whether there is an appropriate dose or interval to provide benefit regarding fracture risk. We aimed to assess the published evidence available to date regarding the putative beneficial effects of vitamin D supplements on fractures and falls according to various dosages and intervals.
Methods
We performed a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies reporting associations between vitamin D supplementation and the risks of fractures and falls in PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane library. Studies with supplements of ergocalciferol or calcitriol, those with a number of event ≤10, or those with a follow-up duration of less than 6 months were also excluded.
Results
Thirty-two studies were included in the final analysis. Vitamin D supplementation with daily dose of 800 to 1,000 mg was associated with lower risks of osteoporotic fracture and fall (pooled relative risk [RR], 0.87; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.78 to 0.97 and RR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.85 to 0.98), while studies with <800 or >1,000 mg/day did not. Also, among intervals, daily administration of vitamin D was associated with the reduced risk of falls, while intermittent dose was not. Also, patients with vitamin D deficiency showed a significant risk reduction of falls after vitamin D supplementation.
Conclusion
Daily vitamin D dose of 800 to 1,000 IU was the most probable way to reduce the fracture and fall risk. Further studies designed with various regimens and targeted vitamin D levels are required to elucidate the benefits of vitamin D supplements. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ukrainian Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults
Nataliia Grygorieva, Mykola Tronko, Volodymir Kovalenko, Serhiy Komisarenko, Tetiana Tatarchuk, Ninel Dedukh, Mykola Veliky, Serhiy Strafun, Yulia Komisarenko, Andrii Kalashnikov, Valeria Orlenko, Volodymyr Pankiv, Oleg Shvets, Inna Gogunska, Svitlana Reg
Nutrients.2024; 16(2): 270. CrossRef - Vitamin D Supplementation: A Review of the Evidence Arguing for a Daily Dose of 2000 International Units (50 µg) of Vitamin D for Adults in the General Population
Pawel Pludowski, William B. Grant, Spyridon N. Karras, Armin Zittermann, Stefan Pilz
Nutrients.2024; 16(3): 391. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Limb Fractures in Saudi Children
Lamia Aldhbiban, Fai Alhoshan, Raghad Alomari, Shahad A Almatrafi, Yousef Alanazi, Samir Alsayegh, Haifa Y Alfaraidi, Ayman H Jawadi, Fahad N Aljuraibah
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The interplay of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis: exploring the pathogenesis and pharmacological approaches
Nikhil Gupta, Navjot Kanwar, Anchal Arora, Kavin Khatri, Abhinav Kanwal
Clinical Rheumatology.2024; 43(5): 1421. CrossRef - The multi-faceted nature of age-associated osteoporosis
A.E. Smit, O.C. Meijer, E.M. Winter
Bone Reports.2024; 20: 101750. CrossRef - Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients With Low-Energy Hip Fractures in Accordance With the Mediterranean Paradox
Christos Konstantinidis, Ourania Psoma, Christos Kotsias, Vasileios Panagiotopoulos , Sotiris Plakoutsis, Dimitrios Tsiampas, Dimitrios Vardakas, Dimitrios Giotis
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of vitamin and/or nutritional supplements with fall among patients with diabetes: A prospective study based on ACCORD and UK Biobank
Lingfang He, Tianqi Ma, Guogang Zhang, Xunjie Cheng, Yongping Bai
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Vitamin D and Calcium in Osteoporosis, and the Role of Bone Turnover Markers: A Narrative Review of Recent Data from RCTs
Gavriela Voulgaridou, Sousana K. Papadopoulou, Paraskevi Detopoulou, Despoina Tsoumana, Constantinos Giaginis, Foivi S. Kondyli, Evgenia Lymperaki, Agathi Pritsa
Diseases.2023; 11(1): 29. CrossRef - Recent advances in the identification of related factors and preventive strategies of hip fracture
Yaohui Yu, Yudan Wang, Xiaoli Hou, Faming Tian
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Can Nutrition Contribute to a Reduction in Sarcopenia, Frailty, and Comorbidities in a Super-Aged Society?
Sadao Yoshida, Ryo Shiraishi, Yuki Nakayama, Yasuko Taira
Nutrients.2023; 15(13): 2991. CrossRef - Safety Profile of Vitamin D in Italy: An Analysis of Spontaneous Reports of Adverse Reactions Related to Drugs and Food Supplements
Valentina Maggini, Giada Crescioli, Ilaria Ippoliti, Eugenia Gallo, Francesca Menniti-Ippolito, Adelaide Chiaravalloti, Vittorio Mascherini, Roberto Da Cas, Simona Potenza, Giulia Gritti, Maria Galiulo, Laura Sottosanti, Alfredo Vannacci, Niccolò Lombardi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4726. CrossRef - Cholecalciferol Use Is Associated With a Decreased Risk of Incident Morphometric Vertebral Fractures in Acromegaly
Sabrina Chiloiro, Stefano Frara, Irene Gagliardi, Antonio Bianchi, Antonella Giampietro, Margherita Medici, Agnese Allora, Luigi di Filippo, Maria Rosaria Ambrosio, Alfredo Pontecorvi, Maria Chiara Zatelli, Laura De Marinis, Andrea Giustina
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e58. CrossRef - Proceedings of the 2023 Santa Fe Bone Symposium: Progress and Controversies in the Management of Patients with Skeletal Diseases
E. Michael Lewiecki, Teresita Bellido, John P. Bilezikian, Jacques P. Brown, Azeez Farooki, Christopher S. Kovacs, Brendan Lee, William D. Leslie, Michael R. McClung, Mark L. Prasarn, Deborah E. Sellmeyer
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2023; 26(4): 101432. CrossRef - Diagnosis, prevention and treatment of vitamin D deficiency in adults: Ukrainian experts consensus statement
N.V. Grygorieva, M.D. Tronko, V.M. Kovalenko, S.V. Komisarenko, T.F. Tatarchuk, N.V. Dedukh, M.M. Veliky, S.S. Strafun, Y.I. Komisarenko, A.V. Kalashnikov, V.L. Orlenko, V.I. Pankiv, O.V. Shvets, I.V. Gogunska, S.I. Regeda
PAIN, JOINTS, SPINE.2023; 13(2): 60. CrossRef - Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Level Is Negatively Associated with Fatigue in Elderly Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients
Menglin Pang, Lin Chen, Na Jiang, Mengmeng Jiang, Baofeng Wang, Lili Wang, Xiao-yan Jia
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2023; 48(1): 231. CrossRef - Vitamin D for Clinical Diseases in Women: An Indispensable Factor in Medicine and Dentistry
Dario Calafiore, Leonzio Fortunato, Mario Migliario
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3104. CrossRef - Malnutrition in Older Adults—Effect on Falls and Fractures: A Narrative Review
Malgorzata Kupisz-Urbanska, Ewa Marcinowska-Suchowierska
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3123. CrossRef - Role of vitamin D supplementation in the management of musculoskeletal diseases: update from an European Society of Clinical and Economical Aspects of Osteoporosis, Osteoarthritis and Musculoskeletal Diseases (ESCEO) working group
Thierry Chevalley, Maria Luisa Brandi, Kevin D. Cashman, Etienne Cavalier, Nicholas C. Harvey, Stefania Maggi, Cyrus Cooper, Nasser Al-Daghri, Oliver Bock, Olivier Bruyère, Mario Miguel Rosa, Bernard Cortet, Alfonso J. Cruz-Jentoft, Antonio Cherubini, Bes
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2022; 34(11): 2603. CrossRef - The Relationship of Osteoporosis with Menopause: Review of Article
Hadeel Anwar Alsarraje, *Liqaa Khalel Alhyali
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences and Technology.2022; 14(01): 127. CrossRef
- Ukrainian Consensus on Diagnosis and Management of Vitamin D Deficiency in Adults

- Adrenal Gland
- Adrenal Morphology as an Indicator of Long-Term Disease Control in Adults with Classic 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency
- Taek Min Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Han Na Jang, Man Ho Choi, Jeong Yeon Cho, Sang Youn Kim
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(1):124-137. Published online February 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1278

- 4,251 View
- 126 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Monitoring adults with classical 21-hydroxylase deficiency (21OHD) is challenging due to variation in clinical and laboratory settings. Moreover, guidelines for adrenal imaging in 21OHD are not yet available. We evaluated the relationship between adrenal morphology and disease control status in classical 21OHD.
Methods
This retrospective, cross-sectional study included 90 adult 21OHD patients and 270 age- and sex-matched healthy controls. We assessed adrenal volume, width, and tumor presence using abdominal computed tomography and evaluated correlations of adrenal volume and width with hormonal status. We investigated the diagnostic performance of adrenal volume and width for identifying well-controlled status in 21OHD patients (17α-hydroxyprogesterone [17-OHP] <10 ng/mL).
Results
The adrenal morphology of 21OHD patients showed hypertrophy (45.6%), normal size (42.2%), and hypotrophy (12.2%). Adrenal tumors were detected in 12 patients (13.3%). The adrenal volume and width of 21OHD patients were significantly larger than those of controls (18.2±12.2 mL vs. 7.1±2.0 mL, 4.7±1.9 mm vs. 3.3±0.5 mm, P<0.001 for both). The 17-OHP and androstenedione levels were highest in patients with adrenal hypertrophy, followed by those with normal adrenal glands and adrenal hypotrophy (P<0.05 for both). Adrenal volume and width correlated positively with adrenocorticotropic hormone, 17-OHP, 11β-hydroxytestosterone, progesterone sulfate, and dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate in both sexes (r=0.33–0.95, P<0.05 for all). For identifying well-controlled patients, the optimal cut-off values of adrenal volume and width were 10.7 mL and 4 mm, respectively (area under the curve, 0.82–0.88; P<0.001 for both).
Conclusion
Adrenal volume and width may be reliable quantitative parameters for monitoring patients with classical 21OHD. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long‐term health consequences of congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Riccardo Pofi, Xiaochen Ji, Nils P. Krone, Jeremy W. Tomlinson
Clinical Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Landscape of Adrenal Tumours in Patients with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Mara Carsote, Ana-Maria Gheorghe, Claudiu Nistor, Alexandra-Ioana Trandafir, Oana-Claudia Sima, Anca-Pati Cucu, Adrian Ciuche, Eugenia Petrova, Adina Ghemigian
Biomedicines.2023; 11(11): 3081. CrossRef - Multiplexed Serum Steroid Profiling Reveals Metabolic Signatures of Subtypes in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Jaeyoon Shim, Chang Ho Ahn, Seung Shin Park, Jongsung Noh, Chaelin Lee, Sang Won Lee, Jung Hee Kim, Man Ho Choi
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Outcomes of Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
Anna Nordenström, Svetlana Lajic, Henrik Falhammar
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 587. CrossRef - Congenital adrenal hyperplasia in patients with adrenal tumors: a population-based case–control study
F. Sahlander, J. Patrova, B. Mannheimer, J. D. Lindh, H. Falhammar
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 46(3): 559. CrossRef - Fully automatic volume measurement of the adrenal gland on CT using deep learning to classify adrenal hyperplasia
Taek Min Kim, Seung Jae Choi, Ji Yeon Ko, Sungwan Kim, Chang Wook Jeong, Jeong Yeon Cho, Sang Youn Kim, Young-Gon Kim
European Radiology.2022; 33(6): 4292. CrossRef
- Long‐term health consequences of congenital adrenal hyperplasia

- Adrenal Gland
- Lipid Profiles in Primary Aldosteronism Compared with Essential Hypertension: Propensity-Score Matching Study
- Sun Joon Moon, Han Na Jang, Jung Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):885-894. Published online August 10, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1012

- 3,199 View
- 138 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
There has been controversy regarding the association between primary aldosteronism (PA) and dyslipidemia and few studies considered the effects of diabetes and renal function on lipid metabolism. We analyzed lipid profiles of PA patients and compared them to propensity-score (PS)-matched essential hypertension (EH) patients adjusting for glycemic status and renal function.
Methods
Patients who were diagnosed with PA using a saline-infusion test at Seoul National University Hospital from 2000 to 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. EH patients who had aldosterone-renin ratio (ARR) results were selected as controls. Covariates, including diabetes, were PS-matched for patients with PA, lateralized PA, non-lateralized PA, and high ARR to EH patients, respectively.
Results
Among a total of 80 PA and 80 EH patients, total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) levels were significantly lower in the PA patients than in the EH patients (least-squares mean±standard error: 185.5±4.4 mg/dL vs. 196.2±4.4 mg/dL, P=0.047, for TC; and 132.3±11.5 mg/dL vs. 157.4±11.4 mg/dL, P=0.035, for TG) in fully adjusted model (adjusting for multiple covariates, including diabetes status, glycosylated hemoglobin level, and estimated glomerular filtration rate). There were no significant differences in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels between the two groups. According to increments in aldosterone levels, an increasing tendency of HDL-C and decreasing tendencies of TG and non-HDL-C were observed.
Conclusion
PA patients had lower TC and TG levels than EH patients, independent of glycemic status and renal function. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of saline infusion test and captopril challenge test in the diagnosis of Chinese with primary aldosteronism in different age groups
Kaiwen Sun, Minghui Gong, Yang Yu, Minghui Yang, Ying Zhang, Yinong Jiang, Wei Song
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Meta‐analysis of blood parameters related to lipid and glucose metabolism between two subtypes of primary aldosteronism
Qiu‐Gen Zhu, Feng Zhu
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2023; 25(1): 13. CrossRef - 2023 Korean Endocrine Society Consensus Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Primary Aldosteronism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Jin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Kyong Yeun Jung, Jeongmin Lee, Jong Han Choi, Seung Hun Lee, Namki Hong, Jung Soo Lim, Byung Kwan Park, Jung-Han Kim, Kyeong Cheon Jung, Jooyoung Cho, Mi-kyung Kim, Choon Hee Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 597. CrossRef - The differences of serum lipid profiles between primary aldosteronism and essential hypertension: a meta-analysis and systematic review
Worapaka Manosroi, Pitchaporn Phudphong, Pichitchai Atthakomol, Mattabhorn Phimphilai
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison of saline infusion test and captopril challenge test in the diagnosis of Chinese with primary aldosteronism in different age groups

- Diabetes
- Response: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
- Han Na Jang, Hye Seung Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(1):194-195. Published online March 19, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.1.194
- [Original]
- 3,351 View
- 65 Download

- Clinical Study
- Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
- Han Na Jang, Ye Seul Yang, Seong Ok Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Hye Seung Jung
- Endocrinol Metab. 2019;34(4):382-389. Published online December 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2019.34.4.382
- 5,000 View
- 143 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Conflicting results have been reported on the efficacy of insulin degludec/insulin aspart (IDegAsp) compared to basal insulin in type 2 diabetes. We investigated the effects of changing basal insulin to IDegAsp on glycemic control and sought to identify factors related to those effects.
Methods In this retrospective study of patients from three referral hospitals, patients with type 2 diabetes using basal insulin with hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels less than 11.0% were enrolled. Basal insulin was replaced with IDegAsp, and data were analyzed from 3 months before to 3 months after the replacement.
Results Eighty patients were recruited (52.5% male; mean age, 67.0±9.8 years; mean duration of diabetes, 18.9±8.5 years; mean HbA1c, 8.7%±1.0%). HbA1c levels increased during 3 months of basal insulin use, but significantly decreased after changing to IDegAsp (8.28%±1.10%,
P =0.0001). The reduction was significant at 6 months in 35 patients whose longer-term data were available. Patients with a measured fasting plasma glucose (m-FPG) lower than their predicted FPG (p-FPG) by regression from HbA1c showed a significant HbA1c reduction caused by the change to IDegAsp, even without a significantly increased insulin dose. However, patients whose m-FPG was higher than their p-FPG did not experience a significant HbA1c reduction, despite a significantly increased insulin dose. Furthermore, the HbA1c reduction caused by IDegAsp was significant in patients with low fasting C-peptide levels and high insulin doses.Conclusion We observed a significant glucose-lowering effect by replacing basal insulin with IDegAsp, especially in patients with a lower m-FPG than p-FPG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the efficiency of insulin degludec/insulin aspart therapy in controlling hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a real-life experience
Gökçen Güngör Semiz, İsmail Selimoğlu, Mehmet Emin Arayici, Serkan Yener, Abdurrahman Çömlekçi, Tevfik Demir
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023; 43(4): 544. CrossRef - Low fasting glucose‐to‐estimated average glucose ratio was associated with superior response to insulin degludec/aspart compared with basal insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes
Han Na Jang, Ye Seul Yang, Tae Jung Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Seong Ok Lee, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Hye Seung Jung
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(1): 85. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart (IDegAsp) in Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Brenda C Edina, Jeremy R Tandaju, Lowilius Wiyono
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing time to intensification between insulin degludec/insulin aspart and insulin glargine: A single-center experience from India
Rajiv Kovil
Journal of Diabetology.2022; 13(2): 171. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart Compared with a Conventional Premixed Insulin or Basal Insulin: A Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Hye-Soo Chung, Yoon-Jung Kim, Jae-Myung Yu, Woo-Ju Jeong, Jiwon Park, Chang-Myung Oh
Metabolites.2021; 11(9): 639. CrossRef - Fear of Hypoglycemia in Adults with diabetes mellitus switching to Treatment with IDegAsp Co-formulation to Examine real-world setting: an observational study (The HATICE study)
Ulaş Serkan Topaloğlu, Hatice Kayış Topaloğlu, Melih Kızıltepe, Mesut Kılıç, Sami Bahçebaşı, Sibel Ata, Şeyma Yıldız, Yasin Şimşek
Drug Metabolism and Drug Interactions.2021; 36(2): 129. CrossRef - Response: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
Han Na Jang, Hye Seung Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 194. CrossRef - Letter: Favorable Glycemic Control with Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart after Changing from Basal Insulin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2019; 34:382-9, Han Na Jang et al.)
Sang Youl Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 192. CrossRef - Fear of hypoglycemia in adults with diabetes mellitus switching to treatment with IDegAsp co-formulation to examine real-world setting: an observational study (The HATICE study)
Ulaş Serkan Topaloğlu, Hatice Kayış Topaloğlu, Melih Kızıltepe, Mesut Kılıç, Sami Bahçebaşı, Sibel Ata, Şeyma Yıldız, Yasin Şimşek
Drug Metabolism and Personalized Therapy.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Evaluation of the efficiency of insulin degludec/insulin aspart therapy in controlling hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a real-life experience


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



